Title: Sulphur Condenser Tubesheet
Client: SES
Software used: Ansys Mechanical
Duration: 4 Months
Keywords: sulphur condenser, tubesheet, UHX, ASME BPVC, pressure differential, thermal gradient, solid element, beam element, pipe element
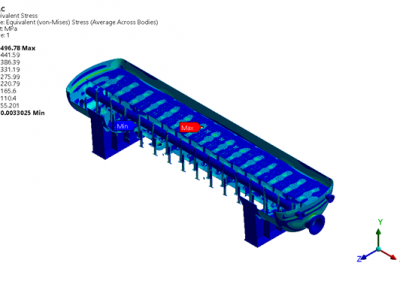
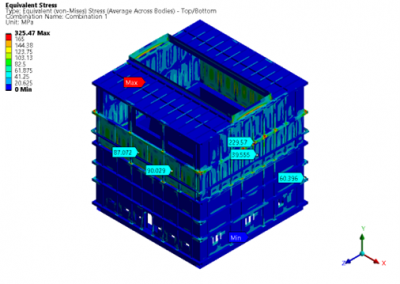
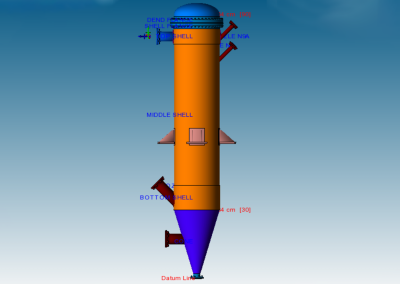
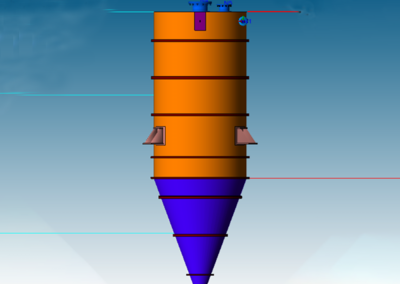
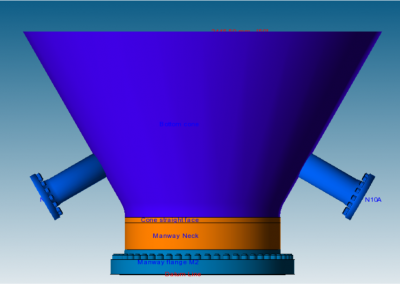
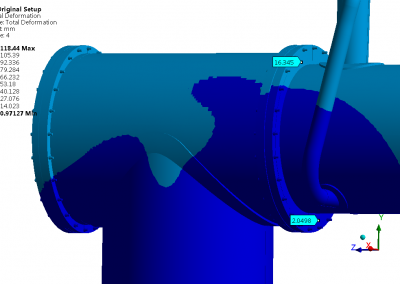
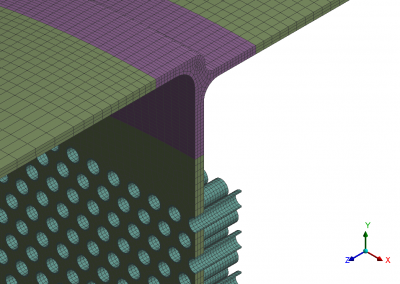
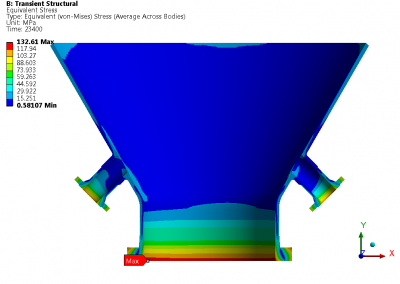
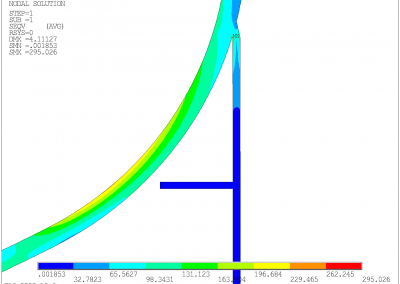
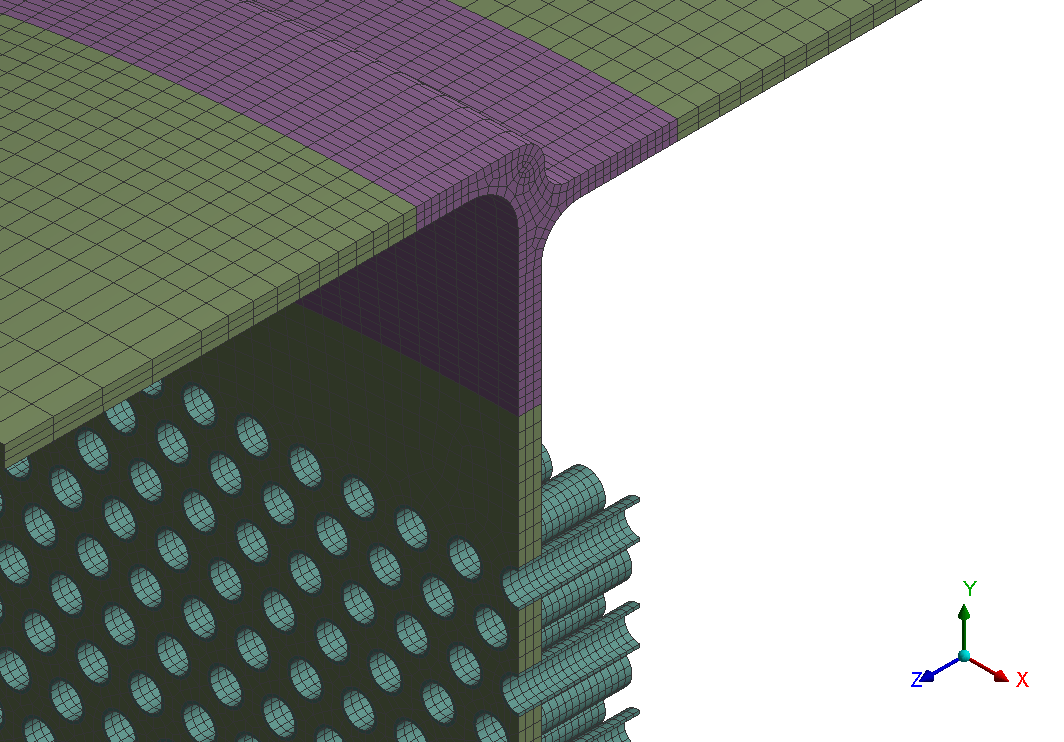
The sulphur condenser is a type of heat exchanger which is a part of the sulphur recovery process in an oil refinery. Shell to tubesheet junction is a critical region in the sulphur condenser, as there is a temperature gradient generated due to different temperatures on the shell side and channel side and the thicknesses of tubesheet and shell are different. The loads acting on a typical tubesheet are the pressure differential across the thickness, the pressure inside the holes and the thermal gradients. The tubes near the junction are modelled with solid elements while the remaining length of the tube is modelled as pipe element which is a special form of beam element. A combination of solid elements and beam elements in the model resulted in reduced size of FE mesh for minimizing computational time. The heat exchanger is designed as per UHX of ASME BPVC Section VIII Div. 1. Hence the load cases for FE analysis are as specified in UHX. Due to two sets of pressure and temperature, there is a number of analysis cases to ensure that the worst-case combination is not neglected. A total of 10 cases are analysed. Linear static structural analysis is performed for design conditions and hydrotest conditions, whereas sequential thermal-structural analysis is performed for operating conditions. Stress linearization is carried out at high-stress locations. The classified stresses are compared with stress limits of design code i.e. ASME BPVC Section VIII Div. 1. For all the locations under given loading conditions, linearized stresses are below the code limit. The tubesheet to shell junction is satisfactory.
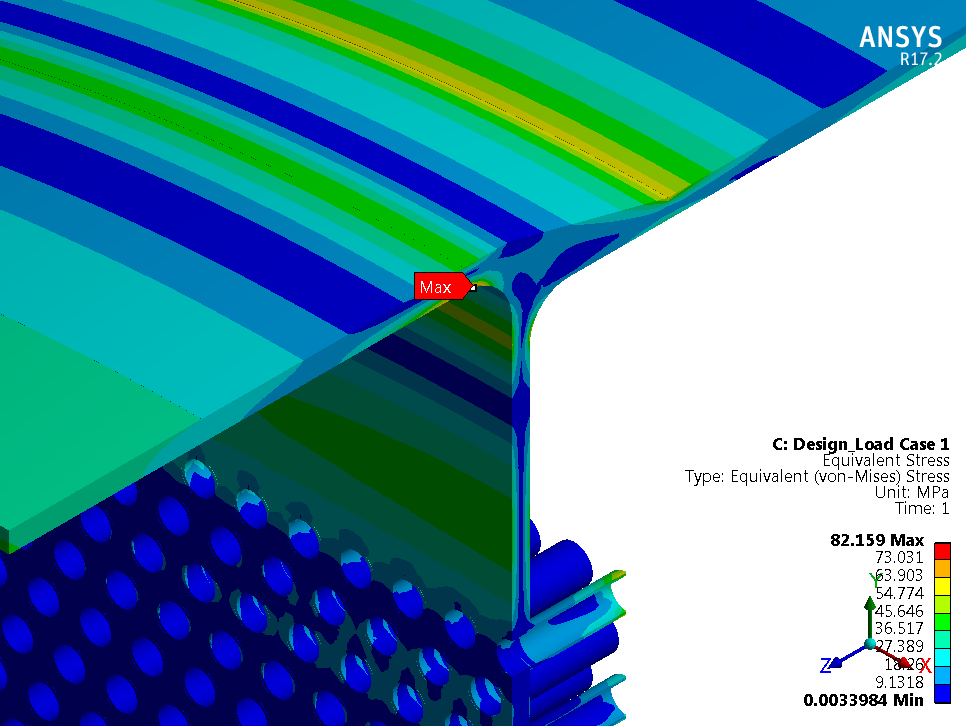
Benchmark: The focus was a shell to tubesheet junction which experiences differential thermal expansion along with the pressure loads. The domain with a large number of tubes was efficiently handled by applying the quarter symmetry of tube and tube sheet configuration and a combination of solid and beam models.
Recent Projects